.ball bearing .roller bearing
Ball bearing have single contact on it rolling race. Friction is less, heat generation is less. Designed for low load application. Thus grease lubrication is enough.
Roller bearing contact point is an entire line, friction is more, generates more heat. Designed for larger load. So it needs extra lubrication.
Bearing types and material:
1. Tin based white metal – Thin or Thick metal
Alloy of 88% Tin(Sn), Antimony(Sb), Copper(Cu), Cadmium
2. Thin shell– 40% Tin Aluminium (Al Sn 40)
Dynamic loading capacity is higher.
Overlayer – Thin layer of Lead (Pb) and Tin (Sn) [for surface conformity embed]
Used for crosshead bearing
3. Flash layer – 100% Tin (Sn)
Corrosion protection (oxidation)
Works on any dry – lubricant
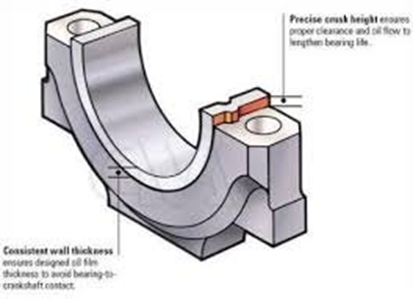
4. Thin shell (have nip crush) – 2-2.5% of journal diameter
Thick shell – 30-60 mm
→ used only for main bearing
Crosshead bearing lower shell made of Tri-metal, steel back, white metal, overlayer
Upper shell – Bimetal – No overlayer
Both have flash layer
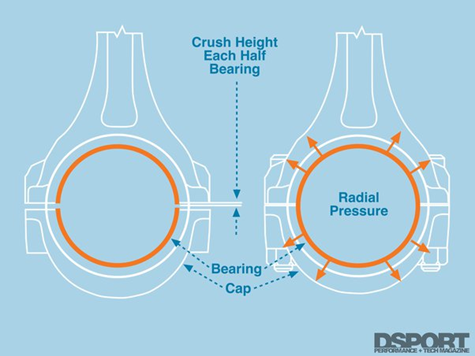
Bearing Nip crush:
It provides a compressive force to the bearing shells resulting in what I would call an interference fit, if it were a one piece cylindrical bearing pressed into a bore. The object is to keep the bearing shells in place without having them spin inside the bore, or work their way out the end of the bore while a rotating shaft is spinning inside.
Broken Roller Bearing in Auxiliary Engine:
Broken Roller Bearing in AE
A broken roller bearing in an AE (Air Eliminator) fuel pump can lead to various issues. Here are some common causes and recommended actions:
Causes
- Lack of Lubrication: Insufficient lubrication can lead to excessive friction, causing the bearing to overheat and eventually break.
- Contamination: Dirt, debris, or other contaminants in the fuel or lubricant can damage the bearing surfaces.
- Misalignment: Incorrect alignment of the pump components can put uneven stress on the bearings, leading to premature failure.
- Overloading: Operating the pump beyond its designed capacity can exert excessive forces on the bearings.
- Wear and Tear: Bearings have a finite lifespan and can break down due to normal wear and tear over time.
- Improper Installation: Incorrect installation procedures, such as using the wrong tools or applying improper techniques, can damage the bearing.
Actions
- Inspection and Replacement: Inspect the damaged bearing and replace it with a new one. Ensure that the replacement bearing is compatible with the pump specifications.
- Lubrication: Ensure proper lubrication of the new bearing and check the lubricant quality and quantity regularly.
- Contamination Control: Implement filtration systems to prevent contaminants from entering the fuel pump system. Regularly check and replace filters.
- Alignment Check: Check alignment of the pump assembly.
