.bottom end bolt .bebf .cpbf .crank pin bolt .crbf .connecting rod bolt failure
.con rod bolt .bolt failure
a) Causes of bottom end bolt failures:
» Stress concentration in way of change of section, damaged fillet, damaged surface finish
» Over stretching / tightening causing permanent damage due to plastic deformation
» Uneven tightening causing overloading of some bolt
» Inadequate pretension causing high fluctuation of stress in bolts and consequently fatigue failure.
» Improper seating of bolt head and nut resulting in bending stress in bolts
» Corrosive attack due to contaminated lube oil.
a) Methods used to tighten the bottom end bolts
.bebt .cpbt .crbt
Hydraulic cylinder & followed up nut:
» During tightening, measurements of extension are essential for correct strength.
» All hydraulic equipment to be checked & calibrate the pressure gauge.
» Tightening must be done more than one stage.
» Final tightening pressure must not be applied at a time.
» Tightening to be done in sequence as per maker’s requirement.
» Tightening must be done in following sequences.
0 0 STBD O 2
0 0 PORT 0 1
Fig: For 4 bolts Fig: For 1 bolt.
Torque spanner:
» First do calibration of torque spanner & adjust the set torque.
» Torque should be applied in more than one stage.
» During final torque applied all work must be done by one person & slowly.
Hand tightening:
» Place one mark on bolt head.
» Place two mark according to angle of final tightening as per maker‘s instruction
» Do that in more than one stages.
In all three types of tightening, it has to be made same. ensure bolts have reached their reference mark on
connecting rod reference mark. Angular accuracy is essential for correct tightening load.
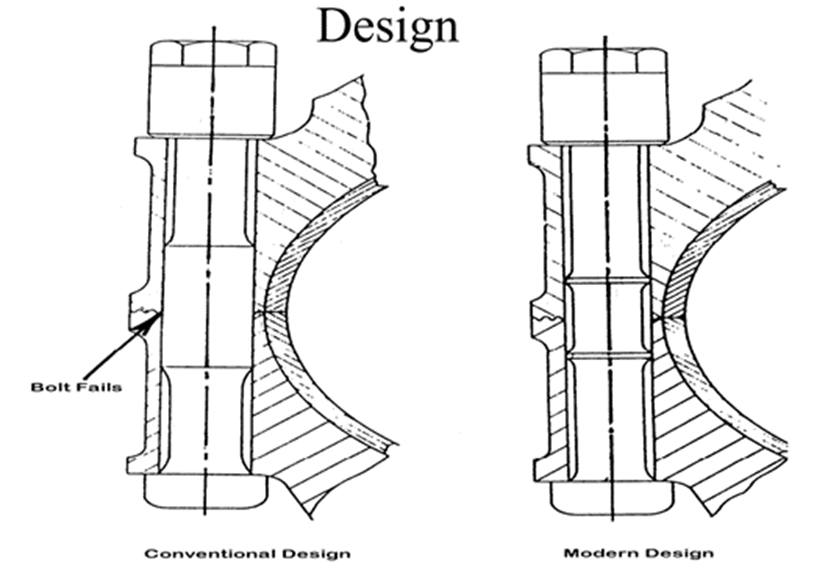
c. Modern design of bottom end bolts:
» Shank diameter is 10% less than core diameter
» Fillet is provided between shank and bolt head to prevent stress concentration
» 3 to 4 threads remain free below contact face of the nut
» High degree of surface finish to prevent stress concentration
» Cold rolling of threads to improve fatigue strength
» Bolt stiffness to be less than bearing housing – less dynamic load on bolt
» High UTS alloy steel with long thin elastic bolts for higher fatigue strength
» Fitted portion to keep as short as possible to prevent stress concentration and to obtain greatest resilience
d) Inspection and maintenance of bottom end bolts:
» Sound testing to detect internal flaws and cracks
» Bolt threads
» Surface finish of bolts
» Fillet area
» Cracks
» Measuring elongation of bolts
» Checking pretension of bolts
» Checking locking device if any