Lube oil sampling procedure?
- Draw samples from a connection that comes directly out of the main oil supply line to the engine.
- Always sample for the same point.
- Sample only when the oil is up to its operating temperature with the engine running.
- Depending upon the draw off point, sufficient amount of oil should be drained out of the line prior to drawing the sample.
- The sample should be filled into a chemically cleaned container after it is rinsed with sample oil and immediately closed.
- The container should be attached with a label as follows:
Records for Sample
- Date of sample drawn
- Point of sample drawn
- Temperature of sample drawn
- Type of oil
- Type of machinery use
- The period of time since the last renewal of oils.
Avoid sampling from places where the oil may be stagnant or have little or no flow, such as sumps, auxiliary smaller pipelines, purifier suction or discharge lines, drain cocks of filters, coolers etc.
Also avoid sampling while engine is stopped.
Microbial Degradation of lubricating oil
.microbial degradation
Stagnant lube oil for long periods in humid conditions can result in bacterial growth due to the presence of water
Indication
- Oil appearance looks slimy and greyish and is indicated by the ‘rotten egg’ odour
Prevention
- Oil must be heated and circulated periodically especially when a ship is laid up
Lube oil properties
.aecc lo .aux eng lo .ae lo
.lo properties .lop
- High oxidation and thermal resistance to perform at elevated temperatures.
- High Viscosity index so that it does not vary much with temperature.
- Appropriate viscosity to meet liner lubrication as well as bearing lubrication 12cst at 100 degree
- High detergency properties so that it softens and takes away all the deposits formed
- High dispersancy properties so that it keeps all the deposits in suspension so that it can be removed easily by purification.
- Higher flash point as it comes into contact with the combustion gases degree
- TBN value according to sulphur content in fuel 10-30 mgKOH/g
- Antifoam properties as the oil tends to have higher deposits
- Extreme pressure and anti-wear additives for maintaining boundary lubrication between piston rings and liner
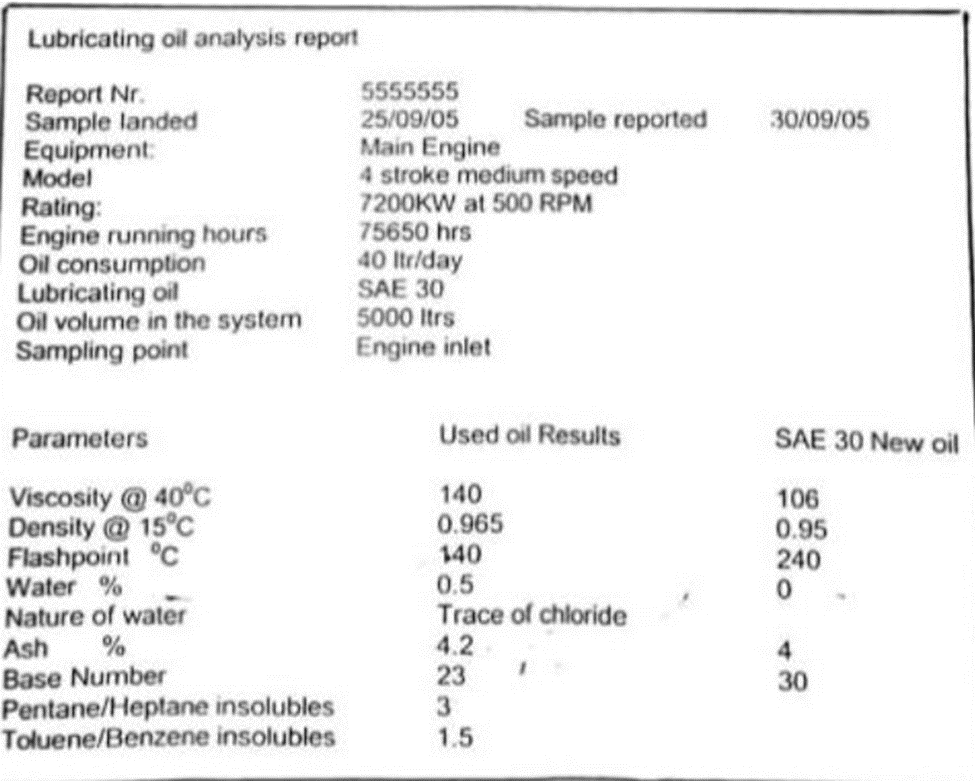
b) Analyze the condition of this oil
Viscosity:
106
Viscosity can increase due to-
- High insoluble content
- HFO contamination due to leaky injectors, worn fuel p/p plunger & barrels
- Piston blow past
- Oxidation due to ageing & high operating temp
- Water contamination (emulsification)
For information: viscosity can decrease by gas oil contamination during prolong running in ECA area.
Density:
0.95
Density can increase due to-
- High insoluble content
- HFO contamination due to leaky injectors, worn fuel p/p plunger & barrels
- Piston blow past
- Water contamination (emulsification)
Flash point:
240 degree C
Flashpoint can reduce, Main suspect FO contamination due to
- leaking injectors, improper combustion, blow-past,
- worn fuel pump plungers & barrels
- Min. 180 deg C
Water:
Should be 0.
Presence of water with trace of chloride Due to
- Bilge leakages likely through
- sump level indicator
- damage diaphragm between sump and engine
- Crankcase breather pipe condensation as atmosphere has saline nature
- Inefficient operation of purifier
- Possible but do not suspect leakages due to steam or engine cooling water leakage as this may increase the base number
- allowable FW content max 0.2%, for short period 0.5%
Ash:
4 mg/kg
Can Increase due to –
- HFO contamination due to leaky injectors, worn fuel p/p plunger & barrels
- Blow past
- Rust in the sump tank
Base number:
30
Can reduce due to
- Insufficient oil volume in circulation
- Irregular top up of sump
- Fuel contamination and sulphur in HFO can reduce TBN
- Max +100%, min -30% of initial value.
Insoluble:
Max 2%.
The amount of insoluble ingredients in the oil is checked as follows.
- Equal parts of oil samples are diluted with [Toluene/benzene] and [pentane / heptane].
- As oxidized oil is only soluble in benzene and not in pentane or heptane the difference in the amount of insoluble is indicatives of the degree of oxidation.
Pentane /heptane Insoluble:
- Indication of oxidation & the metallic deposits/ solid contaminant present
- Max 2%
Toluene/ benzene insoluble:
- Indication of the solid contaminants
- Max 1%
P/H –T/B insoluble:
3 –1.5 = 1.5 is the Indication of the rate of oxidation that has taken place
Limit max. 1%
Main possibility due to iia
- Insufficient volume
- Improper top-up
- Ageing of oil
Batch Purification
.bp .batch purification
.batch purification
When it is done
- Insoluble content is too high
- Recommended in Lub oil analysis report.
- Routinely carried out in dry Dock.
Before commencement transfer in settling tank
- Discusses with master and technical superintendent
- Job risk assessment to be carried out
- Work permit to be taken
- Immobilization permit to be taken
- Ensure the Lube oil settling tank is empty.
- Open the manhole door for setting tank.
- Carry out proper ventilation
- Follow enclosed space entry permit for settling tank.
- Clean the setting tank with lint-free Rags.
- Settling tank walls and top should be free of rust.
- Settling tank heating coil tried out confirm no leakage.
- Drain cock is functioning well
Before purification procedure
- Use the lub oil transfer pump to transfer enter sump oil to the settling tank.
- Take a sample at setting tank for on-board test for water, TBN and viscosity.
- Note down the value for this test.
- Open steam heating to the settling tank and set temperature 60 to 70 degree Celsius
- Allow oil to settle for at least 24 hours
- Drain the tank frequently until water stops coming out
Purification
- Start settling tank to settling tank purification.
- Keep purifier feed rate at minimum on 1/3 of maximum capacity.
- Continue purification as long as time permits.
Sump cleaning
- Open up the void tank manhole cover
- Carry out ventilation for few hours.
- Follow the enclosed space entry permit procedure for void tank.
- Take portable oxygen gas detector, before entry into enclosed space calibrate in atmosphere condition.
- One responsible person must standby outside enclosed space
- Communication must be established with the person outside and the person in bridge.
- After inspection void tank open the manhole cover for sump tank.
- Carry out ventilation of sump tank and follow enclosed space entry procedure separately.
- Entre the sump tank for cleaning.
- Scoop all the sludge and use lint free rags to clean the tank with emphasis on the bottom of the tank.
- Box up the sump tank manhole cover after cleaning.
Transfer LO to sump
- Take a sample at settling tank and carry out on-board test. If the test is satisfactory or engine needs to be ready, start purifier from settling tank to sump tank.
- The void tank manhole cover to be closed only after the sump tank is filled and its manhole has no leakage.
- Mean time clean all LO filters in the system.
Onboard Lube Oil Tests
.lo test
.lube oil test
For all types of lube oils on ships, following Lube oil tests are carried out:
1. Water Content test
5 ml of sample is taken inside digital water content meter mixed with 15 ml of reagent containing paraffin or toluene. Before closing the lid of the digital meter, a sealed sachet containing calcium Hydride is kept and container closed tight. The meter is shaken by hand and the pressure rise due to the chemical reaction in the test container is shown as water percentage in the digital display.
2. pH Test
It is done by using a pH paper which changes colour once in contact with oil and it is then compared with standard values. This test determines the reserve alkalinity of the oil sample.
3. Viscosity Test
This test is performed by using a Flow stick in which two paths are provided for flow of oil side by side. In one path fresh oil is filled and in other side path used sample oil is filled. Now the flow stick is tilted allowing oil on both paths flowing in the direction of the tilt due to gravity. A finish point is provided along with reference points along the flow stick and the position of used oil is checked when fresh oil reaches the finish point.
Q. During watch main engine lube oil level go down, what are your actions?
- Check lube oil sump tank level manually, confirm actual level.
- If low, check for possible lube oil leakages
- Check lube oil purifier
- Check under piston space drain for piston cooling oil leakage.
- Check lube oil pump for possible leakages
- Stop engine if problem found in main engine component and rectify.
- If problem in LO purifier, stop purifier and clean it.
Q. Difference between Stern tube lube oil and crankcase oil
.mecc oil .stern tube oil .st oil
| ME crankcase oil | Stern Tube Lube Oil |
| Excellent thermal and oxidation stability and detergency | Good corrosion protection |
| Excellent deposit control of oil-cooled piston under crown | Excellent wear protection for gears and Bearings |
| Excellent detergency (Clean crankcase) | Excellent viscosity temperature behaviour, high viscosity index (VI) |
| Excellent dispersancy -Extended oil life due to efficient water separating properties () | Miscible with mineral oil and polyalphaolefin gear oil |
| Rust and corrosion properties (anti-oxidant) | Natural dissolving properties |
| Good wear protection | Highest shear stability |
| Approved by major engine manufacturers | Based on renewable resources |
| alkalinity is sufficient to neutralize crankcase contamination (TBN) | Rapidly biodegradable (> 60% acc. to OECD 301 B) |
| High resistance to ageing | |
| Good air release | |
| Good foaming properties | |
| Optimally suited for high and low temperature Use |
LO Emulsification:
.lo emulsification .emulsification .lubricating oil emulsification
Lube Oil Emulsification:
Definition:
– When water is dispersed/penetrated lube oil in the form of small droplets.
– Water droplets remain in an oil layer in a stable form
– Properties of emulsified oil are very different from pure oil
Indications:
1. Stable water content after purification
2. Unusual smells (Rotten eggs)
3. Sliminess of the oil, apparent in crankcase with paint discoloration/removal
4. Heat exchanger performance falling
5. More frequent filter/valve clogging
6. Pitting of tank surface (sump tank)
7. Corrosion of unprotected steelwork, journals, fuel pipes, injector (4 stroke engine)
Causes:
1. Water contamination due to leakages in:
– Exhaust v/v
– Liner
– Cylinder Piston (if water cooler piston)
2. Using wrong gravity disc in L.O. purifier
– Maintain oil-water interface too close to clean oil outlet
3. Condensation due to high humidity
4. Leakage through sump diaphragm due to over tightening or fretting
5. Leakage of bilge:
– Through sounding gauge
– Through expansion bellows fitted between engine & tank top
6. Leakage of L.O. cooler (Tube or gasket)
7. Purifier sealing water solenoid valve leaking
8. Mist box drain choked or Rainwater accumulation in mist box
9. Lube oil purifier steam heater leakage.
Effects:
1. Deterioration in lube oil properties
2. Reduction in load carrying capacity.
3. Reduction in cooling effect.
4. Sludge formation
5. Corrosion in various parts of machinery
6. Worst of all leading to microbial degradation
Corrective/Preventive Actions:
1. Identify & rectify the actual source of leakage (root cause)
2. Centrifuge at optimal throughput and maintain temperature at about 80°C
3. Monitor through shipboard lube oil test for water
4. Batch purification at 1st opportunity
Batch Purification Procedure:
1. Discuss with master & technical manager
2. Immobilization permission
3. Risk assessment carried
4. Discussion in toolbox meeting
5. Relevant work permit to be made
6. Proper ventilation of L.O. settling TK
7. Enclosed space entry permit before entering L.O. sett TK
8. Inspect L.O. sett. TK (Top & walls should be rust free)
9. Clean with lint free rags
10. Sett TK heating coil to be pressure tested for leakage
11. Sett. TK drain cock must be functioning properly
12. Transfer all sump oil to sett. TK from sump by using L.O. transfer p/p
13. Take a sample from sett. TK for onboard lube oil test for water, TBN, Viscosity & spot test
14. Note down the values of this test
15. Steam open for sett TK heating. Maintain temp. 60-70°C
16. Allow oil to settle at least 24 hours
17. Drain the TK frequently until water stops coming
18. Clean the purifier before use & monitor
19. Start purification from sett. to settling TK
20. Keep purifier at optimal throughput and temperature at about 90°C
21. Continue purification for as long as time permits
22. If onboard test result come satisfactory, send sample for lab analysis for detailed test
Sump Cleaning:
1. Open void tank manhole cover & do proper ventilation
2. Prepare enclosed space entry permit upon satisfactory gas test
3. Enter void tank and open sump tank manhole cover
4. Again do proper ventilation & enclose space entry permit made after gas test
5. Enter lub oil sump tk for cleaning
6. Scoop off all the sludge & use lint free rags to clean tank with emphasis on the bottom and loose rust at the ceiling
7. Box up sump tk manhole door
8. Void tk manhole cover to be closed only after sump tk is filled and its manhole has no leakage
9. Take sample from L.O. sett. tk for shipboard lube oil test. If test result is satisfactory and engine needs to be ready, start purification from setting to sump tk
10. Simultaneously, clean all lube oil filter & coolers in the system
11. Update the work done on PMS. Make enough photographic evidence
12. Make a clear report & send it to office
Vessel Options:
1. Upon satisfactory test result from onboard test & shore analysis, discussing with office, vessel may use the oil from sett. TK or dispose it
– Can add partial amount of fresh new oil upon office approval
2. Use fresh batch of new oil with complete charge in sump
Note: It is advisable to use one or more crankshaft bearings at earliest opportunity if the symptoms of emulsification are visible.
