.rotary cup burner .rcb
As the name suggests, this burner comprises a burner nozzle which is covered by a rapidly rotating cone. The fuel oil is carried on to a nozzle which is centrally located within the rotating cone. As the fuel oil moves along the cup due to absence of centripetal force, the oil film becomes thinner in its course as the circumference of the cup increases.
Ultimately, the fuel is discharged from the tip of the rotating cone in the form of fine atomized spray.
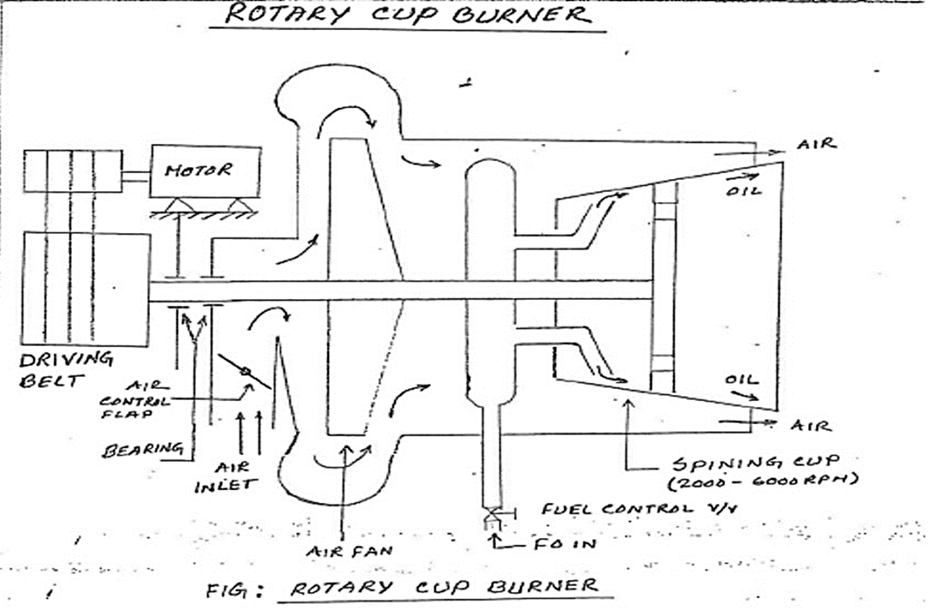
The spinning cup offers the following advantages:
>Wider turn down ratio with lower excess air
> Low 02 levels
> No requirement for atomising air or steam
> Low fuel pressure requirements to an extent that gravity flow is sufficient
> Stable flames achievable with very low fuel flows although maximum flow limited by size of cup. This, allied to being limited to side firing making the design more suitable for smaller installations.
Maintenance of rotary cup burner –
- Clean the rotating cup
- Check and adjust the belt tension between the motor and rotating shaft
- Clean carbon deposited on the electrode ignite and adjusts the gap
- Clean pilot burner nozzle and filter
- Check the fuel valve and air register ( leakage in joints )
- Check and clean the flame eye glass cover
- Check and clean inspection peep hole glass cover
- Adjust the fuel and air ratio, clean the fuel oil filter
- Check the fuel oil pressure
Why rotary cup burner clearance is important?
Answer:
- If the clearance is high then the flame will move outward and become unstable
- If the clearance is low then the flame will move inward and causes burning to the cup tip.
Boiler turndown ratio defined
Boiler turndown is the ratio between a boiler’s maximum and minimum output. Depending on the burner’s design, it may have a turndown ratio between 5:1 and 10:1 or even higher. A 5:1 turndown means the boiler’s minimum operating load is 20% of the boiler’s full capacity (100% capacity divided by 5). A 10:1 turndown means the minimum operating load is 10% of the full load capacity (100% capacity divided by 10).
What is the function of tertiary air in the rotary cup burner?
Answer: flow of tertiary air can be controlled from outside
- it acts like a sealing air
- During combustion it blows away the product of combustion which helps to cool down the cup burner and reduce carbon formation.
- If the air flow is high, it hamper the initial combustion.
