.star delta
Direct-on-line starters is the most commonly used, the most usual consideration being whether the generator and the distribution system can withstand the starting current. In the case of loads with high inertia (e.g. oil separators) the starting time may also be a factor.
The starting current is 5 – 8 times the full load current and the heating of windings is 25 – 64 times normal due to I2R effect. Furthermore, at the instant of starting, there is not windage and radiation. A long starting period may result in overheating. Representative starting periods may be 15 seconds for a 1.5 kW motor and 25 seconds for a 30 kW motor with an initial starting current of not more than 6 times full load current.
For these reasons, it is desirable not to make repeated successive starts without intervening periods of cooling.
In the starting position, the voltage across each phase windings is 58% of the line voltage as it is star connected, i.e. with consequent reduction in starting current. It is 1/3 the starting than delta.
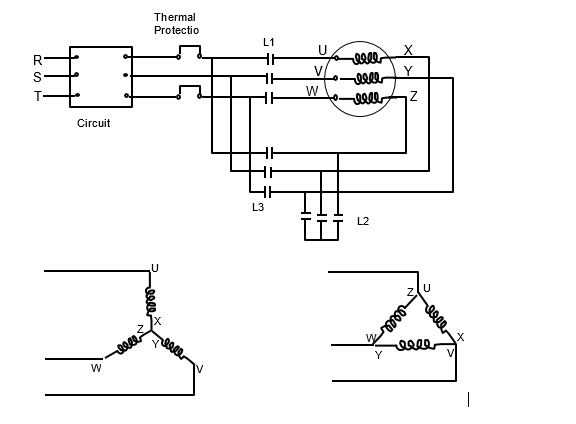
Operation of Star-Delta Starter
- At starting contactor L 2 closes and time delay (not shown) is energized.
- Line contactor L1 closes next.
- Motor starts on reduced voltage due to star connection of motor windings.
- At the end of time delay period, star contactor L2 opens.
- Immediately afterwards, contactor L3 closes.
- Motor now runs on full voltage and on delta connections.
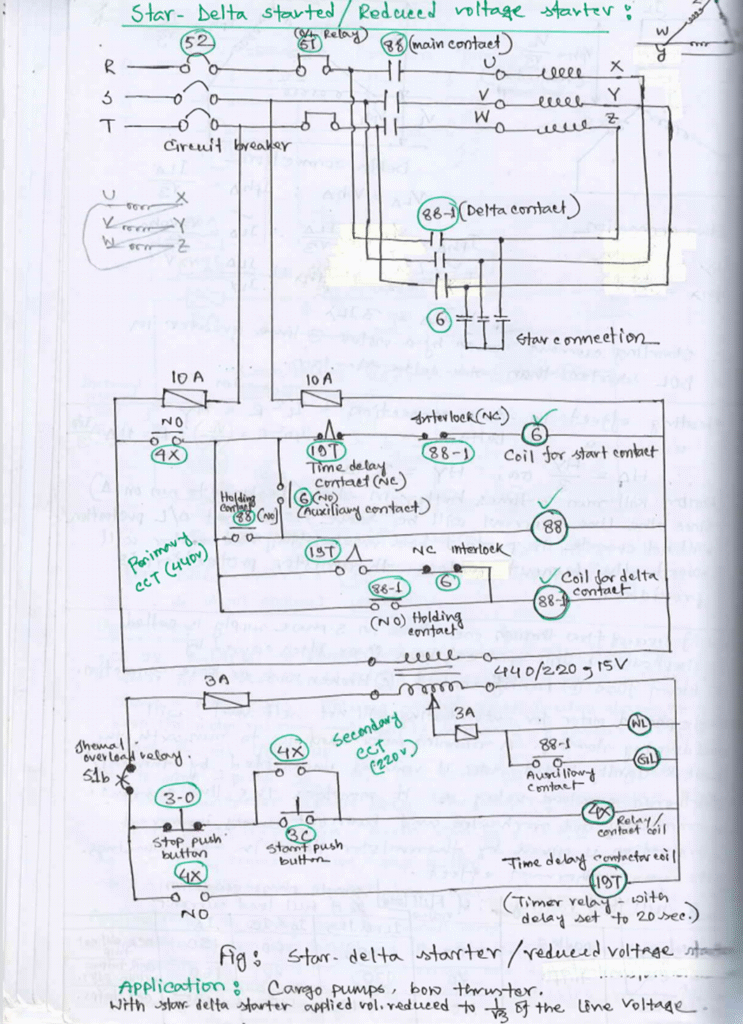
Principle of Operation
operation of the star-delta starter is explained below:
a) When the circuit breaker 52 is switched on, electrical power will be supplied to the transformer and the WL lamp will be lighted up.
b) To start the motor, push-button 3C is depressed and contactor coil 4X is energized. This will close normally-open contact 4X in the transformer primary circuit and energizing contactor coil 6. In the meantime, normally open contact 4X in the transformer secondary circuit will also close thus energizing time-delay contactor coil 19T.
c) When contactor coil 6 is energized:
Main contacts 6 in the main motor circuit will close to form the star connection.
- Normally open auxiliary contact 6 will also close thus energizing contactor coil 88.
- Normally closed contact 6 will open to act as an electrical interlock preventing contactor coil 88-1 from being energized.
d) When contactor coil 88 is energized:
i. Main contacts 88 in the main motor circuit will close and the motor begins to run in star connection.
ii. Normally-open auxiliary contact 88 will also close acting as a holding contact.
e) After the pre-set time delay:
- Normally-closed contact 19T will open thus de-energizing contactor coil 6. This causes the star-connection to open and the normally-closed contact 6 to close back.
f) When contactor coil 88-1 is energized:
i. It will close the main motor circuit contacts 88-1; thus, the motor now runs in the delta connection.
ii. Holding contact 88-1 will also close.
iii. Normally-open auxiliary contact 88-1 closes to light up the GL lamp.
iv. Normally-closed contact 88-1 will open to prevent contactor coil 6 from energizing thus acting as an electrical interlock.
To stop the motor, depress push-button 3-0.
g) Protective devices installed in the circuit are thermal overload relay 51 and fuses.
Effect of Full Voltage Starting and Reduced Voltage Starting
- With full voltage starting, as used in direct-on-line starters, very large current surges of 6 – 8 times full load current occurs.
- With starting of large motors using direct-on-line starters, large voltage dip takes place. This voltage disturbance may result in malfunction of other electrical equipment connected to the supply.
- Reduced-voltage starters, such as the star-delta starter or the autotransformer starter, are used to start large motors, e.g. cargo pumps and bow thrusters.
- With star-delta starters, the applied voltage is reduced to of the line voltage at start. If this is done, both starting torque and starting current are reduced to 1/3 of what they would have been had the motor been switched direct-on-line from the main.

6. For example, suppose a squirrel cage motor is such that if switched on to the mains it develops 90% of its normal full load torque and takes 6 times its normal full load current from the mains. On star-delta starting, it would develop 90/3 i.e. 30% of its normal full load torque and takes 6/3 times its normal full load current.
